Japanese grammar opens doors to a deeper understanding of Japan’s culture and language. Unlike English, Japanese has a unique structure, politeness levels, and use of particles, making it a fascinating but challenging journey for learners. Whether you’re aiming for basic communication or advanced fluency, mastering grammar is an essential step.
This guide will walk you through the best approaches to learning Japanese grammar, from foundational steps to advanced techniques, and help you achieve your language goals.
1. Start with the Basics: Understanding Japanese Alphabets
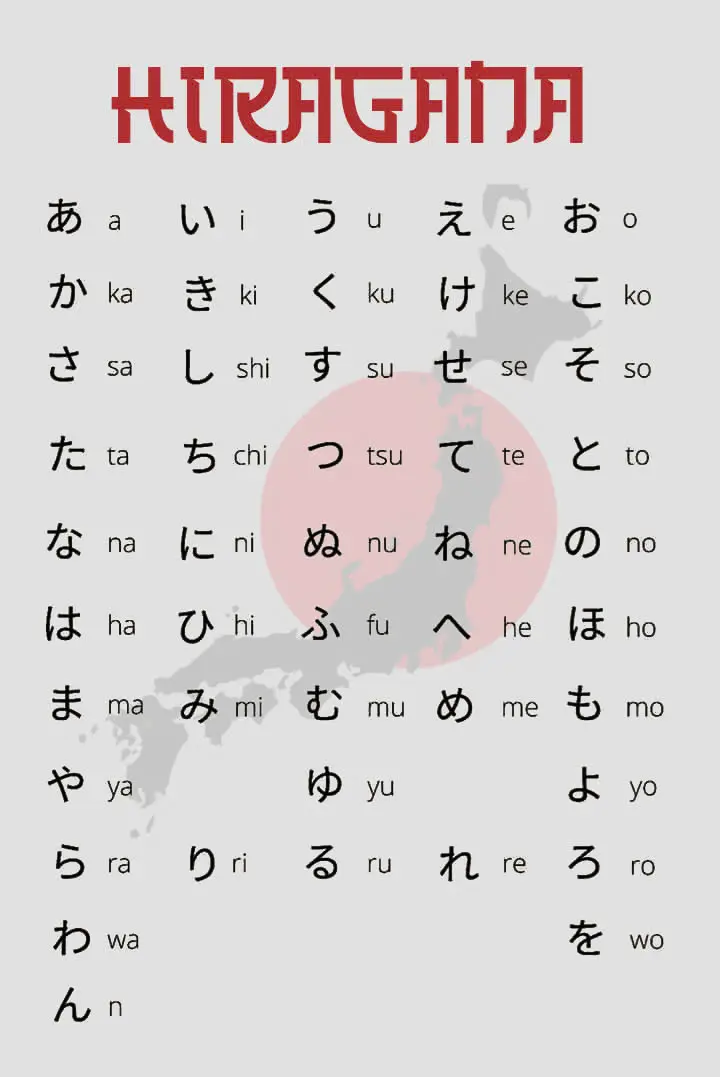
Before diving into grammar, mastering Hiragana, Katakana, and basic Kanji is essential. These writing systems form the backbone of Japanese grammar.
Hiragana and Katakana
- Hiragana is used for native Japanese words and grammatical functions.
- Katakana is reserved for foreign words, names, and emphasis.
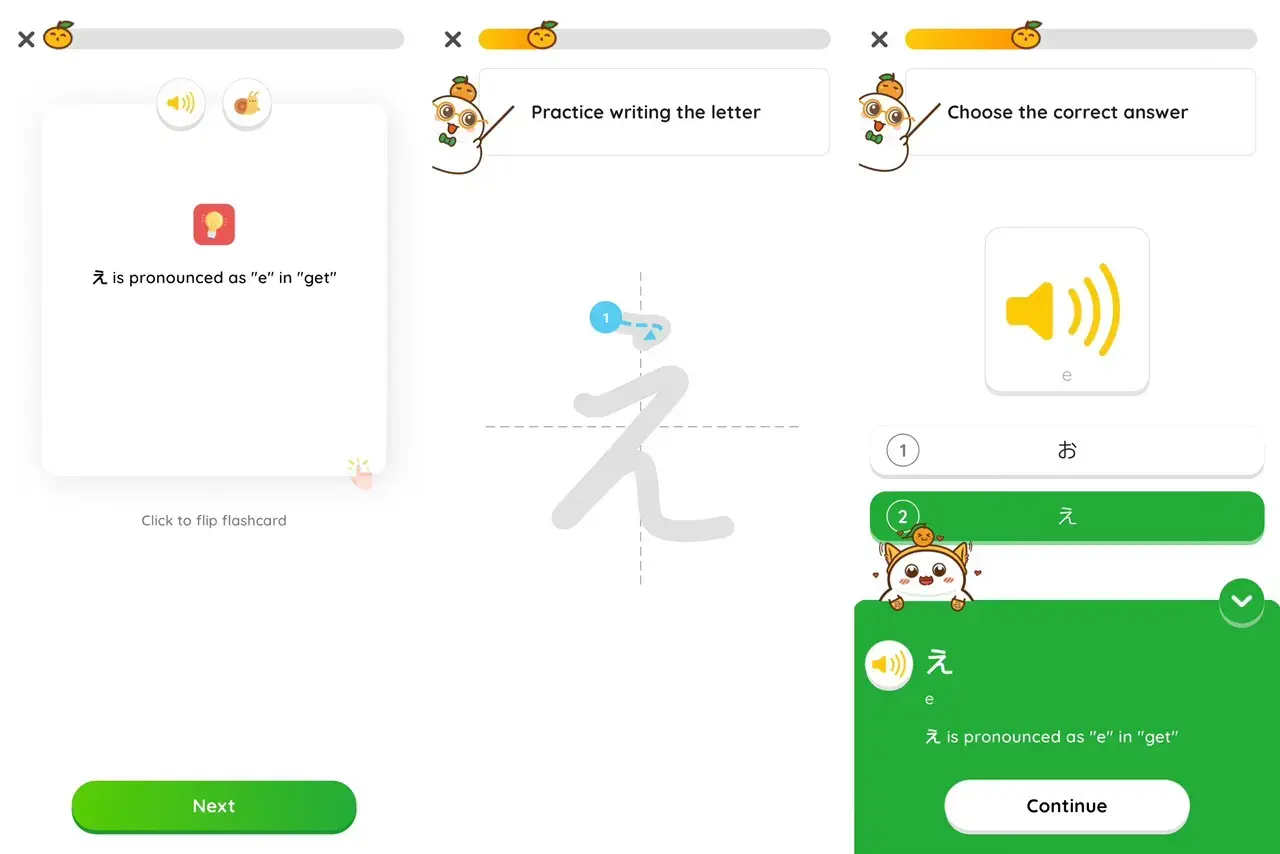
Learning these alphabets allows you to read and write sentences, making grammar learning smoother. Apps like MochiKana are perfect for this stage, offering interactive lessons with mnemonics, flashcards, and a Spaced Repetition System (SRS) to retain knowledge effectively.
Kanji Basics
- Kanji represents words or ideas and is crucial for understanding grammar in written form.
- Start with the most common Kanji and focus on their meanings and pronunciations.
2. Explore Japanese Grammar Rules
Japanese grammar revolves around three key principles:
a. Subject-Object-Verb (SOV) Structure
Japanese sentences follow the SOV order, unlike English’s Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) structure.
- Example:
- English: “I eat sushi.”
- Japanese: “I sushi eat” (私は寿司を食べます).
b. The Role of Particles
Particles are essential for sentence construction. They indicate relationships between words.
- Common particles:
- は (wa): Topic marker.
- が (ga): Subject marker.
- を (wo): Object marker.
- で (de): Location or means marker.
c. Verb Conjugations and Politeness Levels
- Japanese verbs change based on tense, mood, and politeness.
- Politeness levels include plain form (informal) and polite form (formal).
Understanding these foundational rules will help you build sentences confidently.
3. Use Textbooks to Learn Grammar Systematically
Textbooks provide structured lessons and examples, ideal for beginners. Popular choices include:
- Genki I & II: Covers essential grammar, vocabulary, and exercises.
- Minna no Nihongo: Focuses on Japanese-only explanations, great for immersive learning.
- Japanese for Busy People: Practical for learners with limited time.
Follow these books step-by-step, practicing exercises and revisiting lessons regularly to solidify your understanding.
4. Combine Grammar Learning with Vocabulary and Kanji
Learning grammar alongside vocabulary and Kanji makes your study more practical and comprehensive.
Building Vocabulary
- Use flashcards to memorize new words.
- Group vocabulary into themes like food, travel, or family for easier recall.
Mastering Kanji
- Start with JLPT N5 Kanji for basic fluency.
- Practice writing Kanji to reinforce memory.
- Apps like MochiKanji use SRS to help you review and retain Kanji effectively.
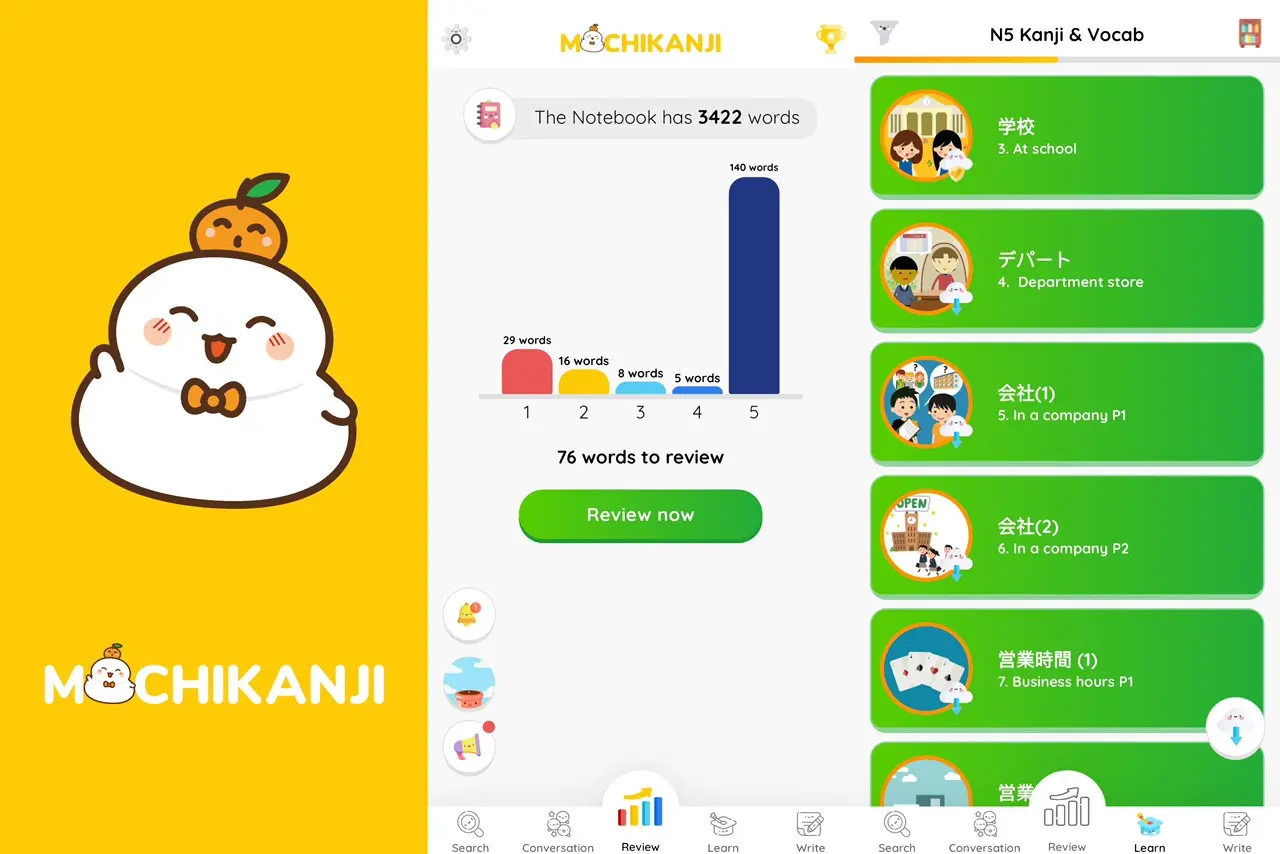
Learning Kanji and vocabulary is made easy using MochiKanji, which uses a spaced repetition method (SRS) to guarantee long-term memory. Applying newly learned grammatical rules to practice sentences utilizing the vocabulary and Kanji you acquire can help you integrate your understanding. To strengthen memory, go over language and Kanji on a regular basis using flashcards.
Integrate new grammar rules into sentences using the vocabulary and Kanji you’ve learned.
5. Practice Makes Perfect: Tips for Applying Grammar
a. Writing Practice
Writing helps reinforce grammar rules and sentence structures.
- Maintain a grammar journal to note down rules and create example sentences.
- Write short essays, diary entries, or practice sentences daily.
b. Listening Practice
Listening exposes you to natural grammar usage in context.
- Recommendations:
- Podcasts: JapanesePod 101 offers lessons with grammar explanations.
- Anime and Movies: Observe grammar in dialogue and mimic sentence patterns.
c. Speaking Practice
Speaking allows you to apply grammar actively.
- Use platforms like HelloTalk or Italki to practice with native speakers.
- Focus on forming sentences rather than perfect grammar initially.
6. Leverage Advanced Methods: Spaced Repetition System (SRS)
SRS is a proven method for retaining vocabulary, Kanji, and grammar. Apps like MochiKanji provide:
- Timely reviews to strengthen memory.
- Notifications for “Golden Time,” the optimal moment to review material.
By dedicating just 20 minutes daily, you can internalize grammar rules faster.
7. Understand Unique Features of Japanese Grammar
a. Politeness Levels
Japanese grammar changes based on formality:
- Plain form: Used among friends or in informal settings.
- Polite form: Essential for interactions with strangers or superiors.
b. Sentence Endings
Sentence-ending particles convey nuances like emotion or politeness:
- よ (yo): Adds emphasis.
- ね (ne): Seeks agreement.
c. Omissions
Subjects are often omitted if understood from context, making sentences concise yet context-dependent.
8. Overcoming Challenges in Japanese Grammar
Mastering Japanese grammar can be challenging due to:
- Complex writing systems: Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji require consistent practice.
- Politeness levels: Using the correct level of politeness takes time and experience.
- Word order: Adjusting to SOV structure may feel unnatural initially.
To overcome these hurdles:
- Break your learning into manageable goals.
- Review regularly to reinforce understanding.
- Immerse yourself in Japanese through media and conversations.
9. Recommended Resources for Grammar Mastery
Here are additional tools to support your grammar learning:
- Tae Kim’s Guide to Learning Japanese Grammar (online resource).
- BunPro: A grammar-focused SRS app.
- MochiKanji: Combines Kanji, vocabulary practice in one platform.
Conclusion
Mastering Japanese grammar is a gradual process, but with the right approach and tools, it becomes manageable and enjoyable. Begin by understanding the basics, build a strong foundation with textbooks, and practice regularly through writing, speaking, and listening.
Integrate innovative methods like SRS for better retention, and don’t forget to immerse yourself in Japanese culture for contextual learning. With dedication and consistency, you’ll achieve your grammar goals and unlock the richness of the Japanese language.
So, start your grammar journey today—がんばって (Ganbatte)!